Featured Projects
Stochastic Network-Level Life Cycle Assessment for Flexible Pavement (In progress)
Client: Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) via University of Massachusetts Amherst
Introduction: Numerous initiatives have been established to reduce pavement emission and greenhouse gases (GHG). While advancements were made in the domain of product footprint and project-level pavement life cycle assessment (LCA), network-level LCA has been limited to a handful of research studies. TEST has partnered with the University of Massachusetts Amherst to integrate these technical developments in support of GHG reduction strategies and goals set by transportation agencies at a network level.
Scope:
- Preparation of a framework for flexible pavement network LCA.
- Data collection and analysis.
- Uncertainty quantification.
- Multi-objective optimization.
- Preparation of two network LCA case studies.
Outcomes: This study will improve the readiness level of network pavement LCA, supporting GHG reduction strategies and goals set by states.

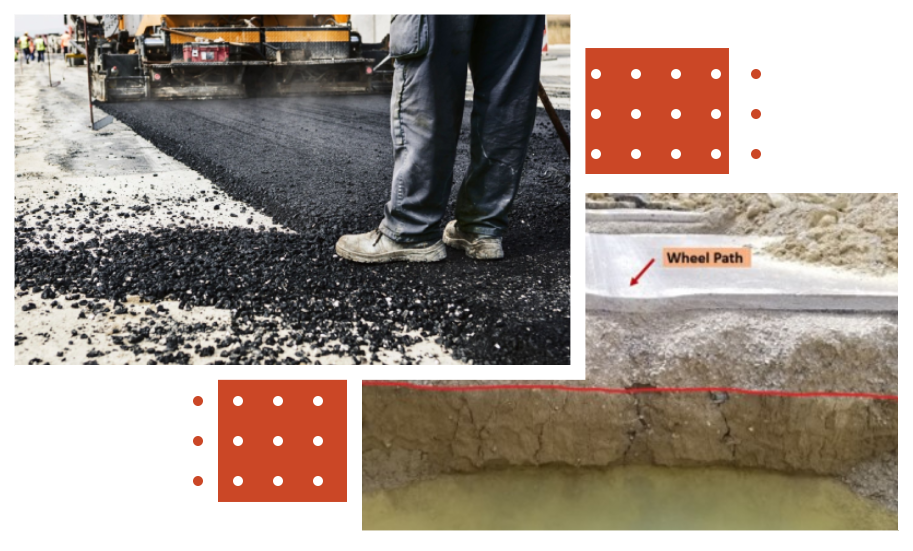
Inverted Pavements Review and Case Studies

Client: Federal Highway Administration (FHWA)
Introduction: Inverted pavement is a design strategy that can lead to economic savings and environmental benefits. Unlike the traditional layering order of base layers, which typically places an unbound granular aggregate base layer before a cement treated base layer, inverted pavements reverse this sequence, with the cement-treated base layer placed before the unbound granular aggregate base layer. While common in South Africa, inverted pavements are relatively uncommon in the United States. In this project, TEST aimed to develop a state-of-the-technology synthesis and assess the use of inverted pavements in the U.S.
Scope:
- Review of national and international literature on research, best practices, and experiences related to inverted pavements.
- Analysis of pavement construction and performance data from eight inverted pavement sections across the U.S.
- Life cycle cost analysis (LCCA) and environmental life cycle assessment (LCA) for selected case studies.
Outcomes: This project investigated best practices for construction and maintenance of inverted pavements drawing on international and national experiences. Findings and recommendations were disseminated through a report, a webinar, and a Transportation Research Board (TRB) workshop.
Click here to see the webinar.
Click here to see the report.
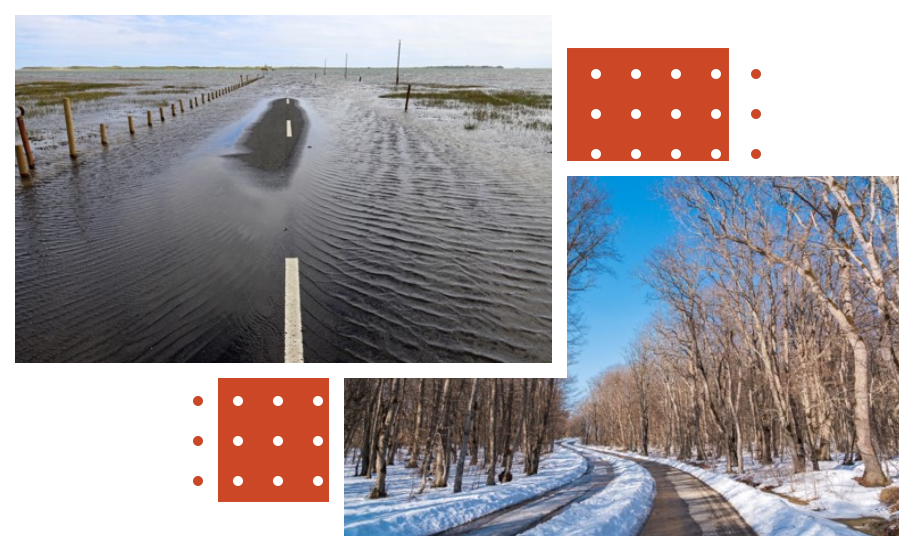
Resilience of Flexible Pavements Following Flooding and Freeze-Thaw Events
Client: National Asphalt Pavement Association (NAPA)
Introduction: Pavement performance can be significantly impacted by flooding and freeze-thaw cycles. The objective of this project was to identify effective flexible pavement solutions resistant to moisture-susceptible environments.
Scope:
- Review of mechanisms through which moisture affects flexible pavement performance.
- Review of flexible pavement design and construction practices aimed at minimizing moisture damage risk.
- Analysis of construction and performance data from five case studies where flexible pavements demonstrated resilience following flooding and/or freeze-thaw events.
Outcomes: The project summarized flexible pavement solutions that have demonstrated resilience to moisture. The findings of the study were disseminated through a report, a technical brief, a webinar, and a Transportation Research Record publication.
Click here to see the webinar.
Click here to see the report.
Click here to see our publication in the Transportation Research Record journal.

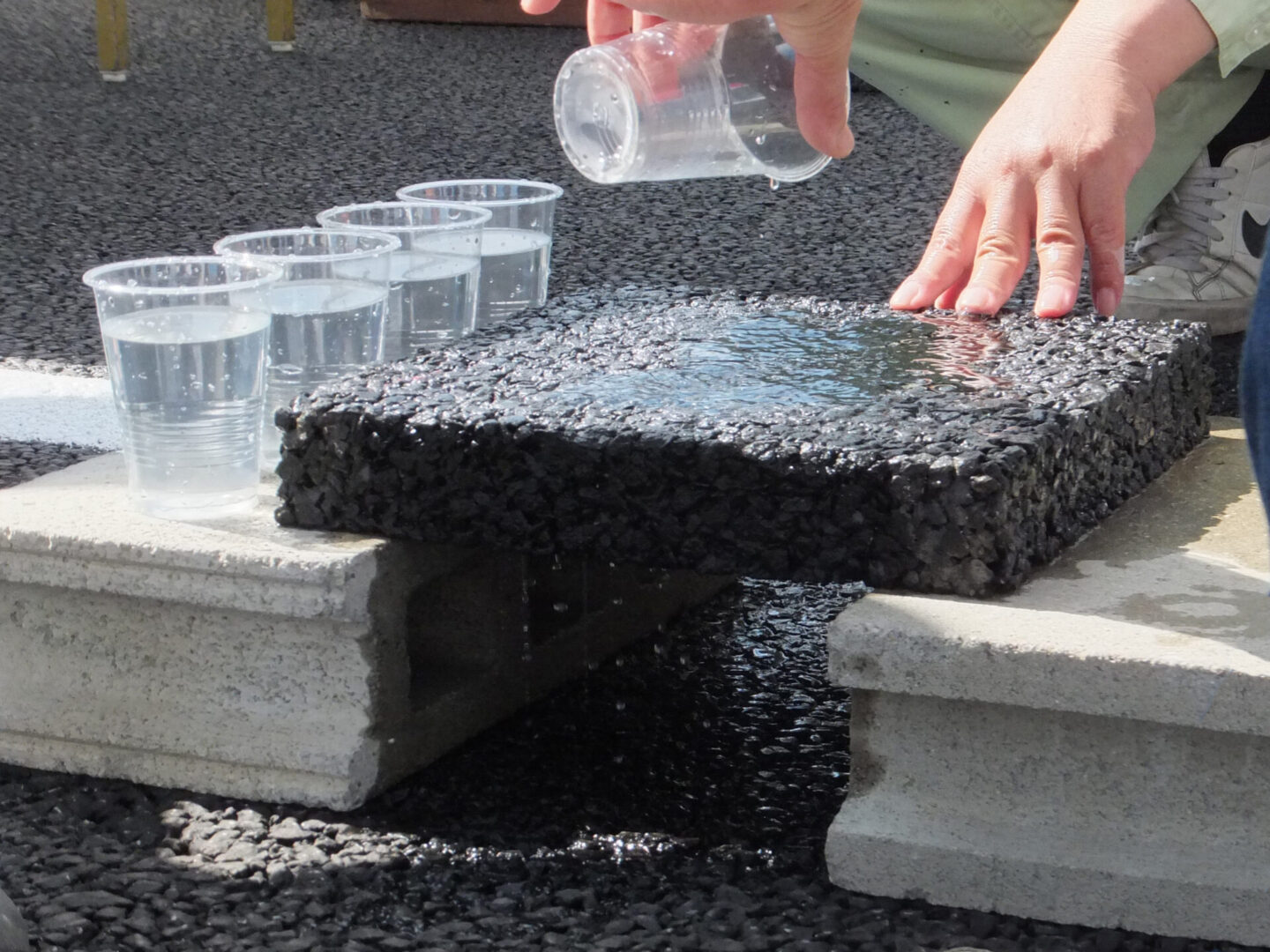
A Review of Permeable Pavements Design and Use

Client: Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) via Engineering & Software Consultants, LLC
Introduction: Impervious paved surfaces pose significant challenges to water management in urban areas and could exacerbate the impact of storms and heat waves on communities. Constructing permeable pavement systems (PPSs) offers a range of benefits, including reducing water runoff, minimizing hydroplaning, and reducing freeze–thaw damage and heat island impacts. PPSs also have the potential to generate cost savings by increasing time between rehabilitations. The objective of this project was to summarize the current state of knowledge and practice for the integration of PPSs in roadway design and construction, with a focus on improving mobility resilience.
Scope:
A comprehensive state-of-the-technology review covering:
- The role of PPS in stormwater management.
- PPS systems, design and operation.
- The benefits of using PPS in urban areas.
- PPS implementation and case studies.
- PPS economic and environmental impacts.
- Challenges and opportunities associated with PPS, including knowledge gaps, and potential solutions.
- Available models and best practices for PPS structural and hydrologic design.
Outcomes: The project provided a comprehensive summary of the state-of-the-technology in PPS, encompassing discussions on their benefits, design, operation and impacts. Project deliverables comprised a summary report submitted to Congress and a more detailed report submitted to FHWA.
Selection of New Pavement and Treatment Surfaces for Flexible Pavements in New Brunswick, Canada
Client: Department of Transportation and Infrastructure, New Brunswick (NB), Canada
Introduction: The objective of this project was to assist the NB Department of Transportation and Infrastructure in the selection of new flexible pavements and in scheduling cost-effective treatments over a pavement’s service life.
Scope:
- Literature review on best practices, design and treatments used in NB and similar climate regions.
- Analysis of NB pavement management system data
- Pavement structural analysis using 3D finite element models
- Development of a pavement selection framework and tool
- Development of a pavement preservation treatment selection framework and tool
Outcomes: The deliverables included decision-based tools for pavement design and treatment selection, a webinar, technical memorandums, and a final report summarizing the project's findings and recommendations.

Life-Cycle Assessment of Ultra-Light Foamed Glass Aggregate

Client: AeroAggregates of North America, LLC
Introduction: Ultra-lightweight foamed glass aggregate (UL-FGA) serves as a lightweight and insulating fill material, providing an alternative to expanded shale or clay, foamed concrete, or geofoam. The objective of this project was to conduct cradle-to-gate life-cycle assessment (LCA) analyses for two UL-FGA products.
Scope:
- Collection of relevant data from the manufacturer and secondary data from external databases
- LCA analysis using the SimaPro software to quantify environmental impacts
- Sensitivity analysis to understand the effects of assumptions made in secondary data and energy sources.
Outcomes: The results of cradle-to-gate LCA and sensitivity analyses were reported to help the client understand the environmental impacts of two UL-FGA products and identify potential areas for improvement in production.
Developing and Extending the Service Life of Road Marking Materials
Client: Road and Transport Authority (RTA) of Dubai via Parsons (Dubai, UAE)
Introduction: Pavement markings provide critical guidance to motorists, particularly in dark (non-lighted) conditions. With the advent of connected and autonomous vehicles, the significance of pavement markings will continue to grow. The RTA of Dubai has reported unexpected short life and blackening of thermoplastics used as marking materials. The objective of this project was to investigate best practices in the use of thermoplastic road marking materials to achieve better performance.
Scope:
- Literature review to investigate thermoplastic marking material application methods, performance, and durability; the impact of tires and specifications on pavement markings; and best practices to reduce blackening of pavement markings.
- Preparation of pavement marking application specifications for a test section.
- Preparation of a method statement for sampling pavement marking material.
Outcomes: The deliverables included a literature review report, specifications for pavement marking application, and a method statement for pavement marking material sampling.

PaveElite (Software)

Client: Gallagher Asphalt
Using the right data and software, contractors can optimize their equipment, plants, and personnel resources to efficiently meet their project demands. TEST developed a customized scheduling software called PaveElite, which offers the following benefits:
- Helps contractors plan ahead, by anticipating conflicts among personnel, equipment, and other resources.
- It features user-friendly drag-and-drop functionality.
- Allows viewing of the big picture and all past, present, and pending jobs on a live, dynamic calendar.
- Allows real-time communication for discussing projects, distributing schedules, and sending out last-minute job changes or cancellations.
- Hosted in the cloud, ensuring that information is accessible on desktops and tablets wherever there is internet access.
PaveElite is an innovative cloud-based scheduling software developed by TEST to support pavement construction teams.
ProLCCA (Software)
State and local highway agencies need to make the best use of their limited budgets for roadway construction and rehabilitation projects considering life-cycle economics. TEST has developed ProLCCA, a life-cycle cost analysis (LCCA) tool that offers the following features:
- Holds a comprehensive database of pay items.
- Stores projects online for easy access and future reference.
- Allows comparison of up to five alternative designs.
- Conducts both deterministic and probabilistic analyses.
ProLCCA is a practical LCCA software developed by TEST to help road agencies achieve optimal cost solutions.
SEL2ECT - Sulfur Extended Asphalt Life Cycle Assessment

Client: Saudi Aramco via King Faisal University
Introduction: With the excess of sulfur by-product in numerous oil and gas producing countries, the industry is exploring new markets, such as the partial substitution of petroleum-based asphalt binder with sulfur in the production of asphalt mixtures. The aim of this project was to quantify the potential environmental benefits of extending asphalt mixtures with sulfur by-product using the life-cycle assessment (LCA) methodology.
Scope:
- Collection of local data on construction practices, materials, and standards.
- Development of a comprehensive desktop software (SEL2ECT) to conduct pavement LCA, encompassing design, construction, use, rehabilitation, and end-of-life phases.
- Analysis of multiple scenarios to assess the potential impacts of sulfur extended asphalt mixtures compared to conventional mixtures.
Outcomes: TEST developed a fully customized desktop software for conducting LCA and prepared LCA analyses for sulfur extended asphalt mixtures.
Life Cycle Analysis Pilot Program for the Carbon Footprint of a Roadway in Costa Rica
Client: National Laboratory of Materials and Structural Models, University of Costa Rica (LanammeUCR)
TEST conducted a partial carbon footprint analysis for a major roadway construction project in Costa Rica. Collaborating with local researchers, TEST distributed surveys and gathered information from local contractors and facilities to calculate environmental life-cycle impacts.
Click here to see our publication in the Sustainability journal.
